When you try to enable Windows Firewall Logging via Group Policy you will notice that the Log Files are not created / do not exist.
You configure the GPO to setup logging:
Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security (Right-Click -> Properties)
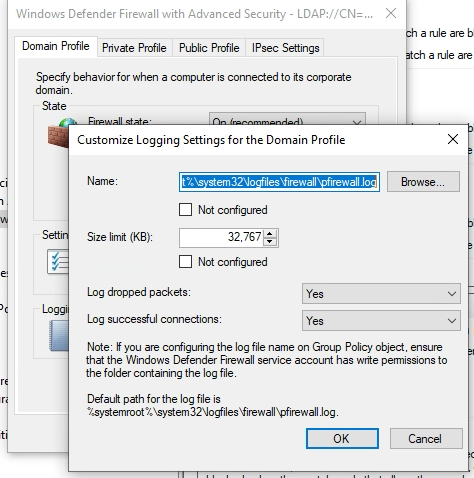
However, no matter how many “gpupdate /force” you run or reboots of the server you do, the “LogFiles” directory still does not contain a “firewall” folder, let alone the actual log files.
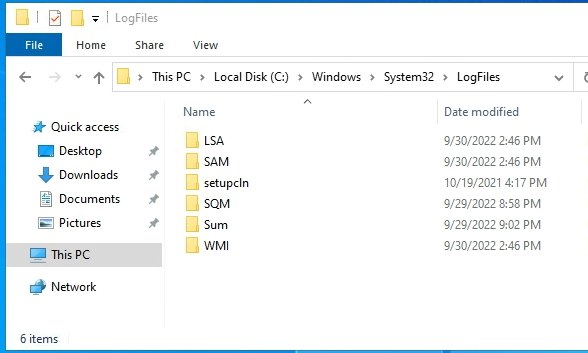
How do we fix this?
One thing you could do if are deploying from a template is configure the template so these files are created. However, this only fixes new server deployments going forward, doesn’t do much for the servers already out there running.
The good news is, the same commands that can be used to fix the template can also fix all the servers that are currently running out there in the wild.
The Fix
In order to make a blog that will work for Server GUI or Server Core I’m going to use netsh firewall commands, run these from an elevated “Administrator” command prompt or PowerShell window.
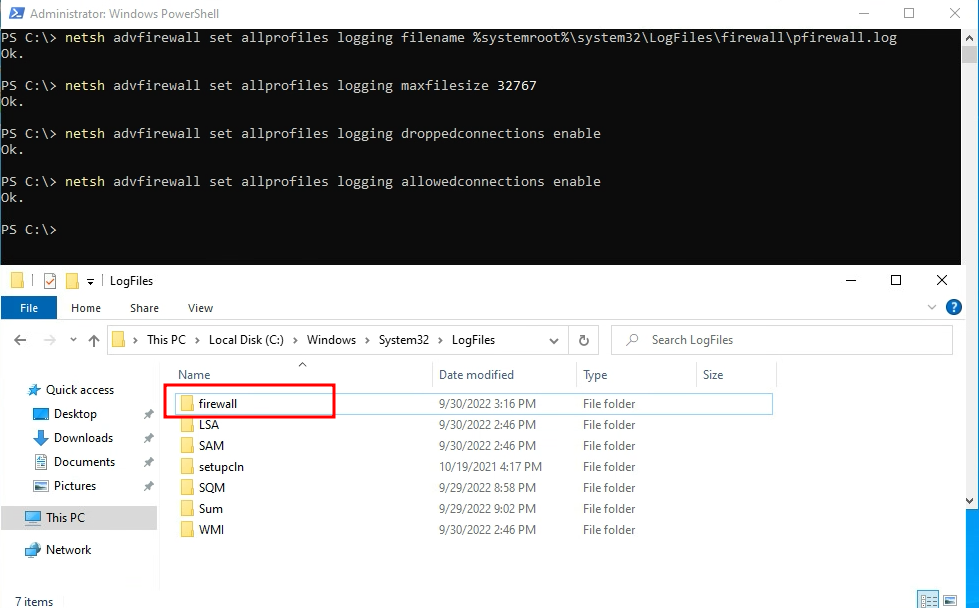
The first command will actually create the folder and files necessary, and group policy should be able to configure everything else.
These commands will create the folder/files, set the maximum file size for the log file to the maximum size allowed by windows, log dropped packets, and allowed packets.
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles logging filename %systemroot%\system32\LogFiles\firewall\pfirewall.log
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles logging maxfilesize 32767
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles logging droppedconnections enable
netsh advfirewall set allprofiles logging allowedconnections enable